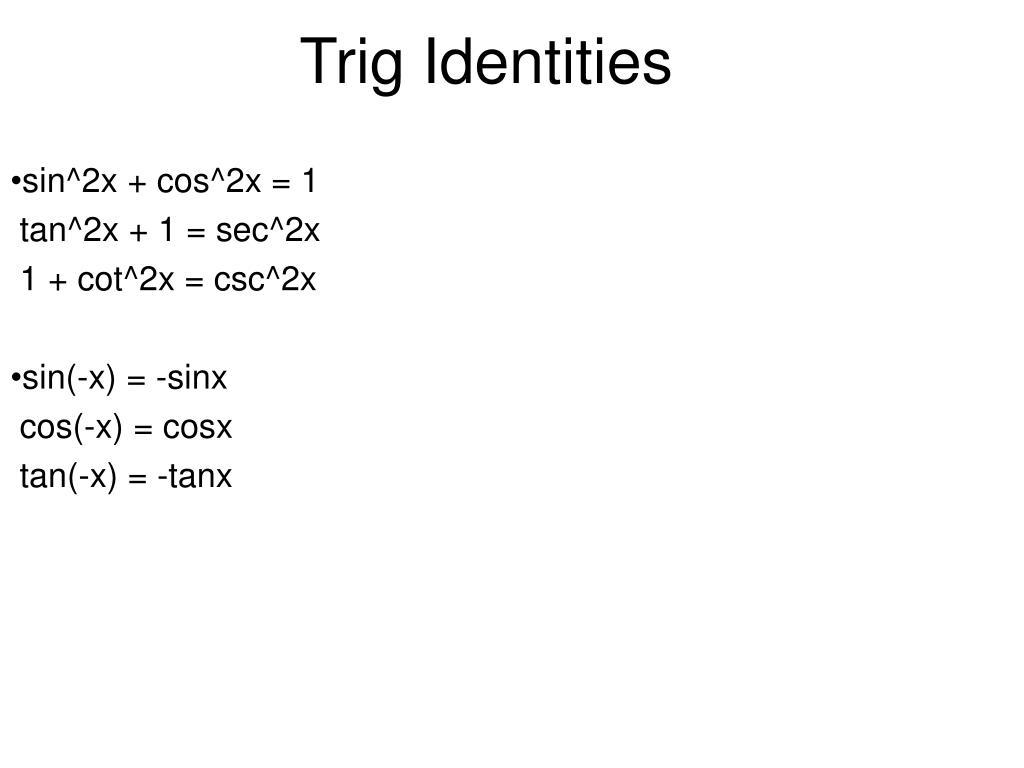
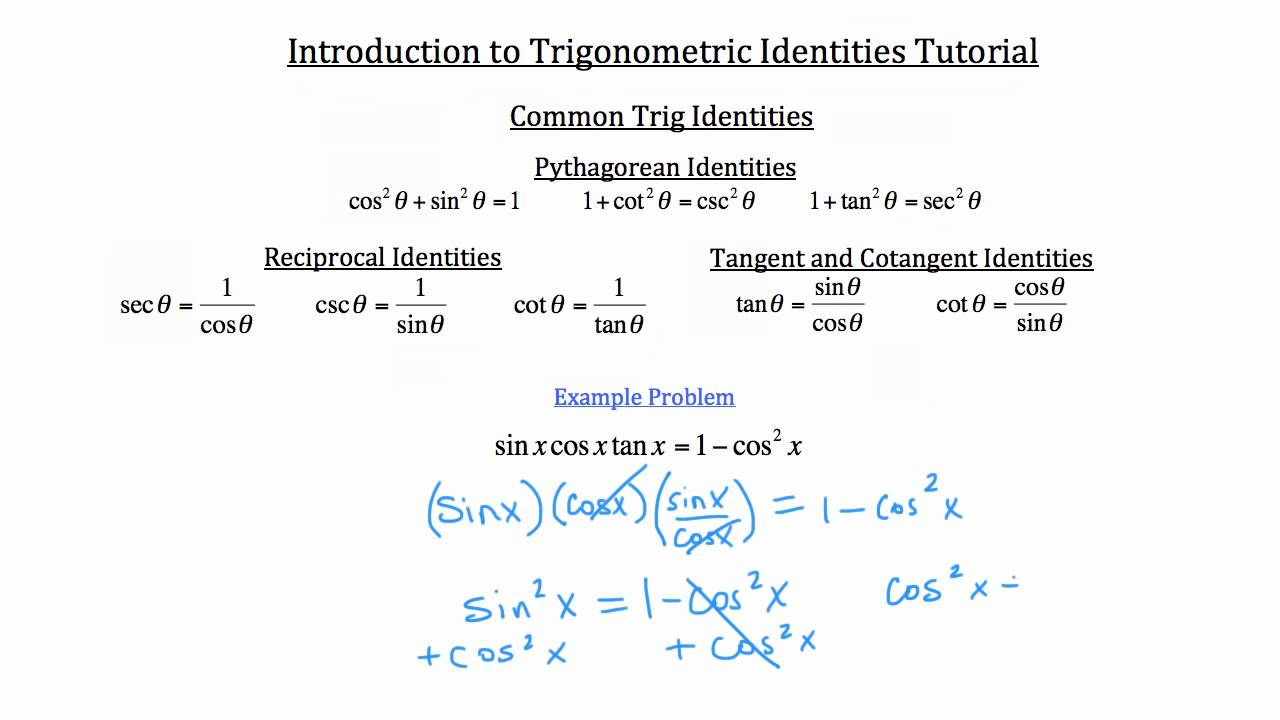
True Start with the well known pythagorean identity sin^2x cos^2x = 1 This is readily derived directly from the definition of the basic trigonometric functions sin and cos and Pythagoras's Theorem Divide both side by cos^2x and we get sin^2x/cos^2x cos^2x/cos^2x = 1/cos^2x tan^2x 1 = sec^2x tan^2x = sec^2x 1 Confirming that the result is an identityTo determine the difference identity for tangent, use the fact that tan(−β) = −tanβ Example 1 Find the exact value of tan 75° Because 75° = 45° 30° Example 2 Verify that tan (180° − x) = −tan x Example 3 Verify that tan (180° x) = tan x Example 4 Verify that tan (360° − x) = − tan x The preceding three examples verify three formulas known as the reductionTrigonometric Identities Worksheet I Prove each identity 1) tanxcos x = sinx 2) cotxsec x = esc x 3) sin x cot x == cos x 4) tan xcsc x sec

List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia
Tan^2 trig identity
Tan^2 trig identity- 1tan^2x=sec^2x Change to sines and cosines then simplify 1tan^2x=1(sin^2x)/cos^2x =(cos^2xsin^2x) Trigonometry Trigonometric Identities and Equations Fundamental Identities 1 AnswerC2 Trigonometry Trigonometric Identities PhysicsAndMathsTutorcom Edexcel Internal Review 1 1 Solve, for 0 < θ < 360°, giving your answers to 1 decimal place where appropriate, (a) 2 sin θ = 3 cos θ, (3) (b) 2 – cos θ = 2 sin2 θ (6) (Total 9 marks) 2 Solve, for –90° < x < 90°, giving answers to 1 decimal place, (a) tan (3x



Ppt Analytic Trig Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Tan(x y) = (tan x tan y) / (1 tan x tan y) sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x cos(2x) = cos 2 (x) sin 2 (x) = 2 cos 2 (x) 1 = 1 2 sin 2 (x) tan(2x) = 2 tan(x) / (1Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Statistics Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal DistributionGet stepbystep solutions from expert tutors as fast as 1530 minutes Your first 5 questions are on us!
Free math lessons and math homework help from basic math to algebra, geometry and beyond Students, teachers, parents, and everyone can find solutions to their math problems instantlyVisit http//ilectureonlinecom for more math and science lectures!In this video I will introduce the halfangle formula tan(x/2)=?Trig identities or Trigonometric identities are actually the mathematics equations which are comprised of trigonometric functionsAnd these trig identities are valid for any estimation of the variable put There are numerous trigonometric identities which are determined by the essential trigonometric functions for instance sin, cos, tan, and so forth
Purplemath In mathematics, an "identity" is an equation which is always true These can be "trivially" true, like "x = x" or usefully true, such as the Pythagorean Theorem's "a 2 b 2 = c 2" for right trianglesThere are loads of trigonometric identities, but the following are the ones you're most likely to see and useTrig identities or a trig substitution mcTYintusingtrig091 Some integrals involving trigonometric functions can be evaluated by using the trigonometric identities and using the identity 1tan2 θ = sec2 θ this reduces to 1 a Z 1dθ = 1 a θ c = 1 a tan−1 x a cTo integrate tan^22x, also written as ∫tan 2 2x dx, tan squared 2x, (tan2x)^2, and tan^2(2x), we start by utilising standard trig identities to change the form of the integral Our goal is to have sec 2 2x in the new form because there is a standard integration solution for that in formula booklets that we can use We recall the Pythagorean trig identity, and multiply the angles by 2




Trigonometric Identities A Plus Topper




Oneclass Tan 0 2 Use Trigonometric Identities To Find The Exacd Value Of Each Of The Following A
The tan squared function rule is also popularly expressed in two forms in trigonometry $\tan^2{x} \,=\, \sec^2{x}1$ $\tan^2{A} \,=\, \sec^2{A}1$ In this way, you can write the square of tangent function formula in terms of any angle in mathematics Proof Take, the theta is an angle of a right triangle, then the tangent and secant areLet's start with the left side since it has more going on Using basic trig identities, we know tan (θ) can be converted to sin (θ)/ cos (θ), which makes everything sines and cosines 1 − c o s ( 2 θ) = ( s i n ( θ) c o s ( θ) ) s i n ( 2 θ) Distribute the right side of the equation 1 − c o s ( 2 θ) = 2 s i n 2 ( θ)2 tan sec sin 1 tan x x x x Microsoft Word trigonometric_identities_with_solutionsdoc Author TrifonMadas Created Date 6/3/15 PM




Ppt Analytic Trig Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Simplify Each Of The Following Trigonometric Chegg Com
In this video I go over a quick proof of the trigonometric identities tan(x y) and tan(x – y) The identity is simple to derive because we can use the iden2 x I started this by making sec 1/cos and using the double angle identity for that and it didn't work at all in any way ever Not sure why I can't do that, but something was wrong Anyways I looked at the solutions manual and they magic out 1 tan x tan 2 x = 1 tanTan is an "odd" identity quotient identity (for tangent) algebra/ simplify 1) 2) cos tan (x) Strategy 1) get rid of the negatives 2) üy to change terms to sin's and COS's 3) simplFy • tan (x) tan x sm x cos x smx cos (x) cosx • cosx • Prove Strategy




While You Wait Trigonometric Identities And Equations Section




Lesson 1 Basic Trig Identities Involving Sin Cos And Tan Trig Precalculus Vol 2 Trig Identities Math Tutor Public Gallery
Periodicity of trig functions Sine, cosine, secant, and cosecant have period 2 π while tangent and cotangent have period π Identities for negative angles Sine, tangent, cotangent, and cosecant are odd functions while cosine and secant are even functions Ptolemy's identities, the sum and difference formulas for sine and cosine1tan2θ=sec2θ 1 tan 2 θ = sec 2 θ The secondTrigonometric identities reciprocal identities pythagorean = x sum and sin x sin tan ± y doubleangle identities 2x = 2 = = x — x — tan xPythagorean identity The basic relationship between the sine and the cosine is the Pythagorean trigonometric identity where cos2 θ means (cos(θ))2 and sin2 θ means (sin(θ))2



1



Inverse Trig Identities Reciprocal Of Trigonometric Function Trig
Trigonometry Identities Examples and Strategies cosine is an "even" identity;Trigonometric Identities Solver \square! Trigonometric Identities Sine, tangent, cotangent and cosecant in mathematics an identity is an equation that is always true Meanwhile trigonometric identities are equations that involve trigonometric functions that are always true This identities mostly refer to
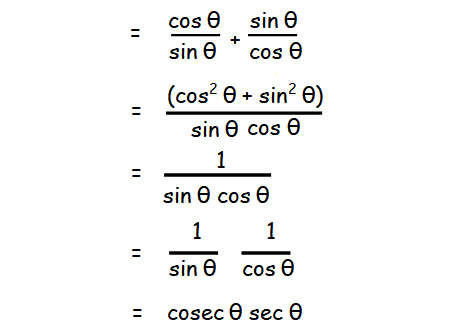



Proving Trigonometric Identities
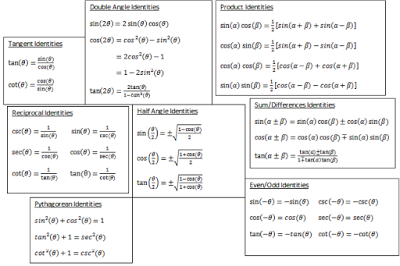



How Do You Verify The Identity Tan2theta 2 Cottheta Tantheta Socratic
Section 71 Solving Trigonometric Equations and Identities 413 Try it Now 2 Solve 2 2sin ( ) 3cos(t t ) for all solutions t 0 2 In addition to the Pythagorean identity, it is often necessary to rewrite the tangent, secant, You can check some important questions on trigonometry and trigonometry all formula from below 1 Find cos X and tan X if sin X = 2/3 2 In a given triangle LMN, with a right angle at M, LN MN = 30 cm and LM = 8 cm Calculate the values of sin L, cos L, and tan L 3In this video I go over the proof of the trigonometry identity tan^2(x) 1 = sec^2(x) The proof of this identity is very simple and like many other trig id
.JPG)



Every Day I M Calculatin I D3 Unit Q Pythagorean Identities



How I Remember Trig Identities Part 2 Beyond Solutions
In mathematics, the inverse trigonometric functions (occasionally also called arcus functions, antitrigonometric functions or cyclometric functions) are the inverse functions of the trigonometric functions (with suitably restricted domains)Specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, and are used to obtain an angle from any ofCos^2 x sin^2 x = 1 sin x/cos x = tan x You want to simplify an equation down so you can use one of the trig identities to simplify your answer even more some other identities (you will learn later) include cos x/sin x = cot x 1 tan^2 x = sec^2 x 1 cot^2 x = csc^2 x hope this helped!Trig identities Trigonometric identities are equations that are used to describe the many relationships that exist between the trigonometric functions Among other uses, they can be helpful for simplifying trigonometric expressions and equations The following shows some of the identities you may encounter in your study of trigonometry



Solving Trigonometric Equations With Identities Algebra And Trigonometry
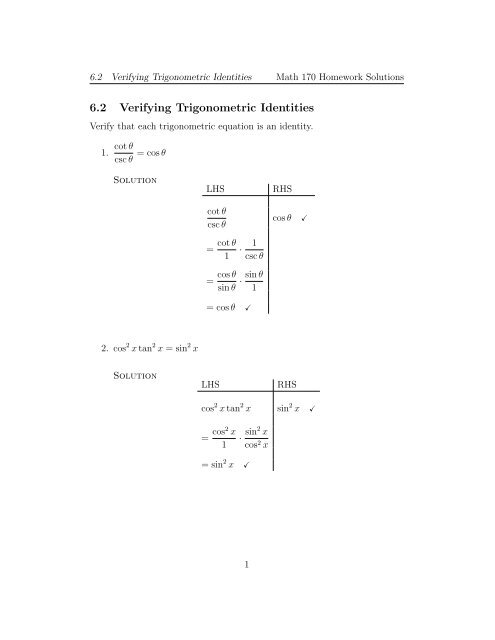



6 2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities
θ = 2 3 − 5 3 = − 2 5 = − 2 5 5 Find the values of the other five trigonometric functions Example 321 2 tan θ = − 5 12, π 2 < θ < π Solution First, we know that \theta is in the second quadrant, making sine positive and cosine negative For this problem, we will use the Pythagorean Identity 1 tan 2Opposite 2 Adjacent 2 = Hypotenuse 2 Dividing both sides by Hypotenuse 2 Opposite 2 /Hypotenuse 2 Adjacent 2 /Hypotenuse 2 = Hypotenuse 2 /Hypotenuse 2 sin 2 θ cos 2 θ = 1 This is one of the Pythagorean identities In the same way, we can derive two other Pythagorean trigonometric identities 1tan 2 θ = sec 2 θIn Trigonometry, different types of problems can be solved using trigonometry formulas These problems may include trigonometric ratios (sin, cos, tan, sec, cosec and cot), Pythagorean identities, product identities, etc Some formulas including the sign of ratios in different quadrants, involving cofunction identities (shifting angles), sum & difference identities, double angle identities




14 2 Trigonometric Identities



Http Www Whsd K12 Pa Us Userfiles 1598 Classes 9713 Trig chapter 5 notes Pdf
In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions, angle functions or goniometric functions) are real functions which relate an angle of a rightangled triangle to ratios of two side lengths They are widely used in all sciences that are related to geometry, such as navigation, solid mechanics, celestial mechanics, geodesy, and many othersSolve the below practice questions based on the trigonometry identities that will help in understanding and applying the formulas in an effective way Express the ratios cos A, tan A and sec A in terms of sin A Prove that sec A (1 – sin A)(sec A tan A) = 1 Find the value of 7 sec 2 A – 7 tan 2 Trig Identities Cheat Sheet When solving, simplify with the identities initially, if you can Trigonometric identities are used to manipulate the trigonometric equations of some specific forms In this video, the Pythagorean identities and the way they are derived are shown In mathematics, there are numerous logarithmic identities



Trigonometric Identities




Summary Of Trigonometric Identities
Trig Cheat Sheet Definition of the Trig Functions Right triangle definition For this definition we assume that 0 2 p Proving the trigonometric identity $(\tan{^2x}1)(\cos{^2(x)}1)=\tan{^2x}$ has been quite the challenge I have so far attempted using simply the basic trigonometric identities based on the Pythagorean Theorem I am unsure if these basic identities are unsuitable for the situation or if I am not looking at the right angle to tackle this problemIn integral calculus, the Weierstrass substitution or tangent halfangle substitution is a method for evaluating integrals, which converts a rational function of trigonometric functions of x {\displaystyle x} into an ordinary rational function of t {\displaystyle t} by setting t = tan ( x / 2 ) {\displaystyle t=\tan (x/2)}



Pythagorean Trigonometric Identities




7 4 Proving Trigonometric Identities In This Unit We Ll Be Using Some Formula S That Are Also Found And Used In Unit 7 2 And 7 3 Here We Ll Be Solving Problems To Show That Both Sides Of The Equation Equal Each Other These Formulas Will Help Solve Some Trig
Trig identity 1tan^2Jul 10, 18 Trigonometric identities are used to manipulate the trigonometric equations of some specific forms In this video, the Pythagorean identities and the way they are derived are shown In mathematics, there are numerous logarithmic identities1tan2 a = sec2 a As it is known that tan a is not defined for a = 90° therefore identity 2 obtained above is true for 0 ≤ AIdentities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Tan^{2} en Related Symbolab blog posts Spinning The Unit Circle (Evaluating Trig Functions ) If you've ever taken a ferris wheel ride then you know about periodic motion,About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators




14 2 Trigonometric Identities
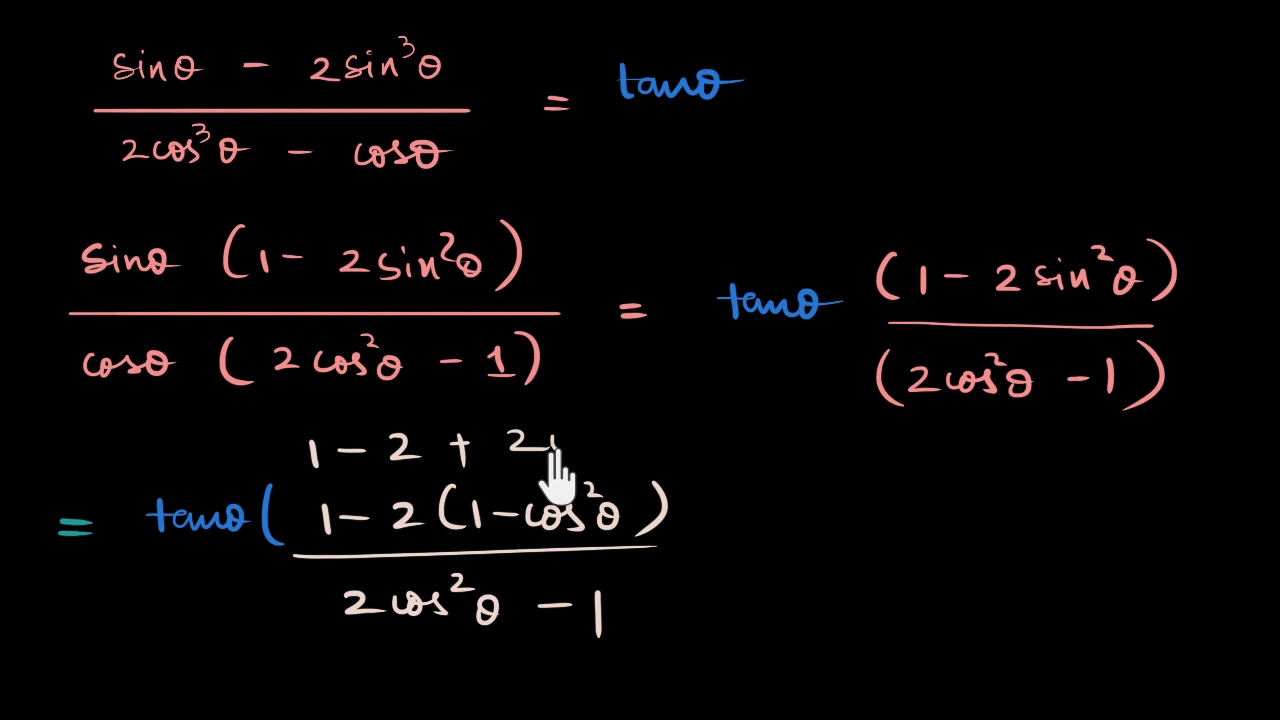



Trigonometric Identity Example Proof Involving Sin Cos And Tan Video Khan Academy
Tan squared trig identityThe key Pythagorean Trigonometric identity are sin 2 (t) cos 2 (t) = 1 tan 2 (t) 1 = sec 2 (t) 1 cot 2 (t) = csc 2 (t) So, from this recipe, we can infer the equations for different capacities additionally Learn more about Pythagoras Trig Identities Dividing through by c 2 gives a 2/ c 2 b 2/ c 2 = c 2/ c 2 This can be simplifiedHow do you find sin if tan=2? `tan^2 theta1=sec^2 theta` `1cot^2 theta=csc^2 theta` Proving Trigonometric Identities Suggestions Learn well the formulas given above (or at least, know how to find them quickly) The better you know the basic identities, the easier it will be to recognise what is going on in the problems Work on the most complex side and simplify it so that it has the same formPeriodicity of trig functions Sine, cosine, secant, and cosecant have period 2 π while tangent and cotangent have period π Identities for negative angles Sine, tangent, cotangent, and cosecant are odd functions while cosine and secant are even functions Ptolemy's identities, the sum and difference formulas for sine and cosine




Establish The Identity 1 Tan 2 Theta 1 Tan 2 Chegg Com



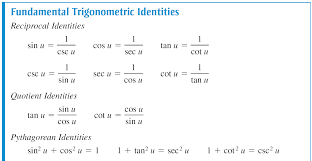
5 1 Fundamental Trig Identities Reciprocal Identities Sin
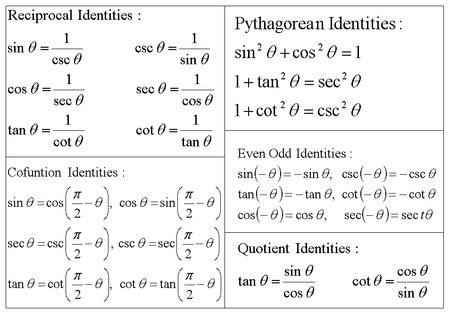
A lot of trigonometric identities don't need to be memorised you can derive them on the fly using the unit circle I'll be covering sin(180 x) = sin x,Trigonometry Identities Reciprocal Identities csc𝜃= 1 sin𝜃 sec𝜃= 1 cos𝜃 cot𝜃= 1 tan𝜃 Pythagorean Identities sin2𝜃cos2𝜃=1 tan 2𝜃1=sec2𝜃 1cot2𝜃=csc2𝜃 Sum & Difference 1−tan tan tan( − )= tan −tan 1tan tan Double–Angle Identities sin 2𝜃=2 sin𝜃 cos𝜃 cos 2 𝜃 = cos 2
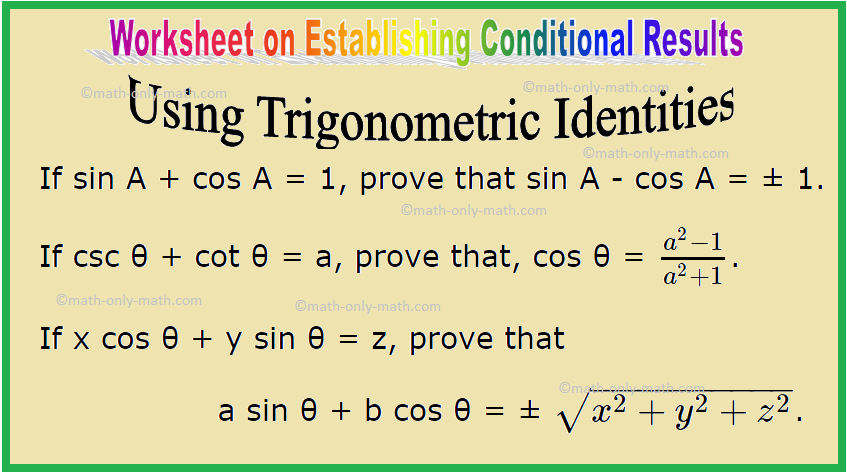



Establishing Conditional Results Using Trigonometric Identities Hints




Math Rescue Trigonometry Proving Trigonometric Identities



What Does It Mean To Prove A Trigonometric Identity Socratic
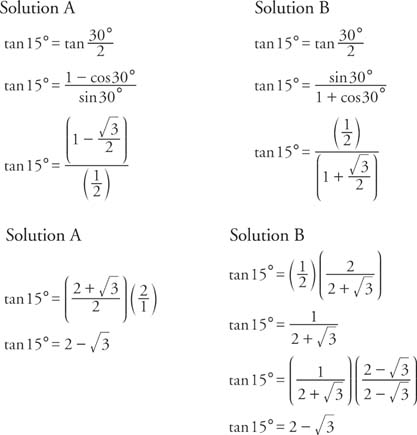



Tangent Identities



6 1 2 Trigonometric Identities




Trigonometric Identities And Examples With Worksheets



Derivatives Of Trigonometric Functions
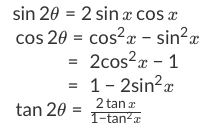



How To Use Double Angle Identities Studypug




13 1 Trigonometric Identities Ppt Video Online Download



Www2 Math Binghamton Edu Lib Exe Fetch Php People Mckenzie Trig Identities Worksheet With Answers 2 Pdf




Trigonometric Identities
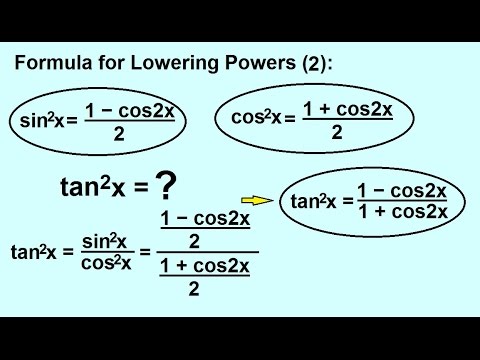



Precalculus Trigonometry Trig Identities 29 Of 57 Formula For Lowering Power Tan 2 X Youtube
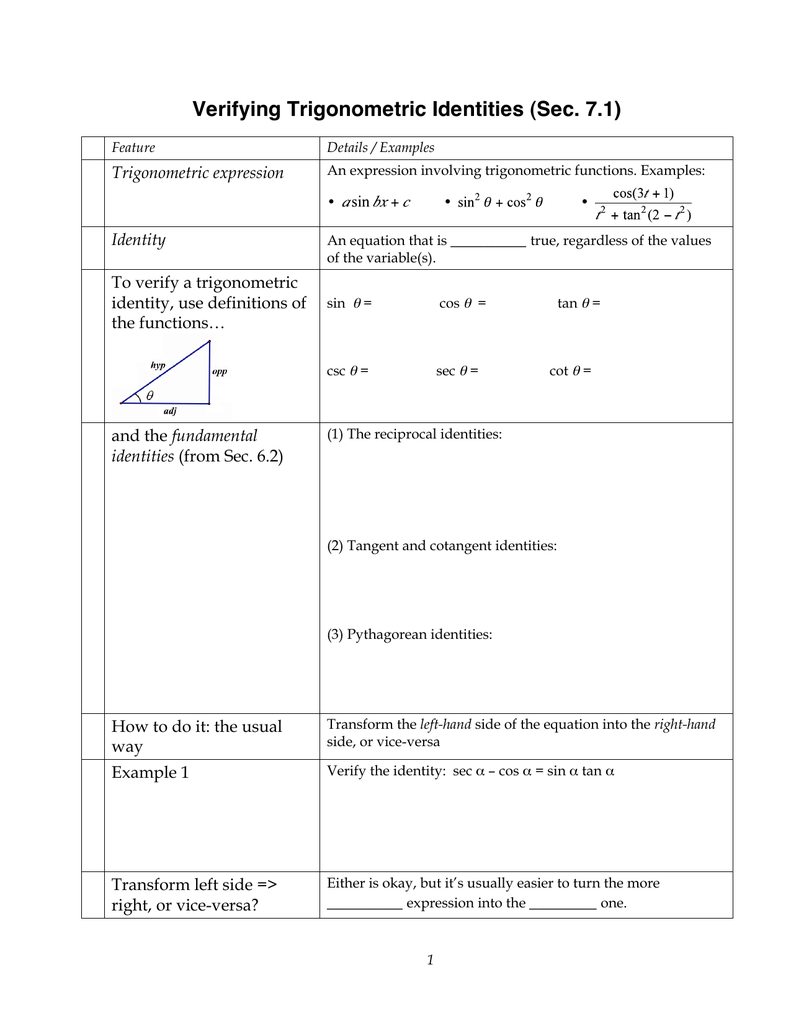



Verifying Trigonometric Identities Sec 7 1 Trigonometric Expression Identity
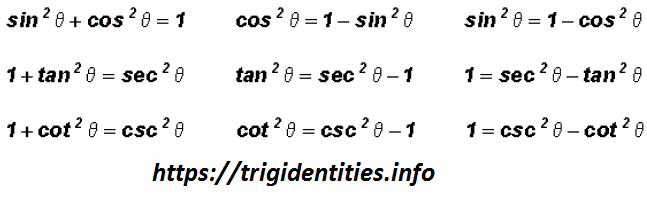



Pythagorean Trig Identities Recall Pythagoras Theorem Trig Identities
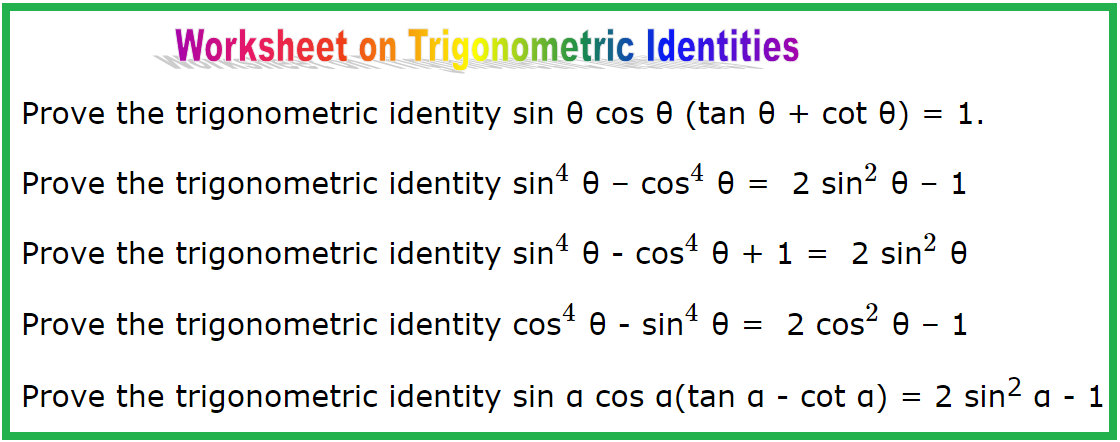



Worksheet On Trigonometric Identities Establishing Identities Hints




Warm Up Prove Sin 2 X Cos 2 X 1 This Is One Of 3 Pythagorean Identities That We Will Be Using In Ch 11 The Other 2 Are 1 Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Ppt Download
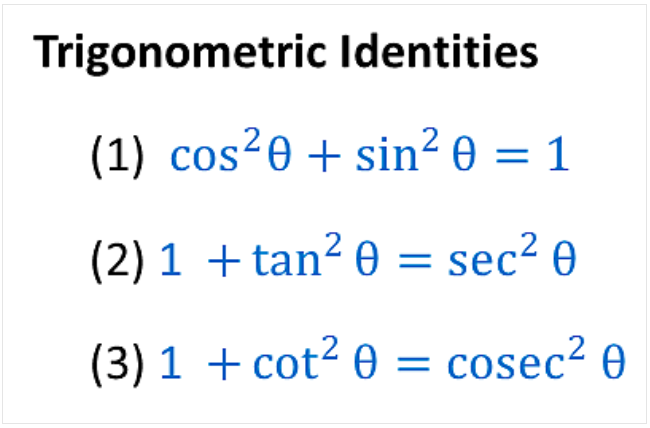



Formula Of Trigonometry Sin Cos Tan Cot Sec Cosec




Trigonometric Identities



How Do You Use The Fundamental Trigonometric Identities To Determine The Simplified Form Of The Expression Socratic




Trig Identities For Pre Calculus Dummies




List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia




Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia



3



7 Proving Ids Trig Functions Identities




Example 1 Verify A Trigonometric Identity The Left Hand Side Of This Identity Is More Complicated So Transform That Expression Into The One On The Right Ppt Download
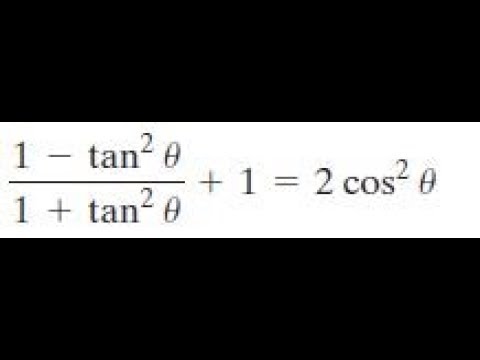



1 Tan 2x 1 Tan 2 X 1 2cos 2 X Youtube




Summary Of Trigonometric Identities
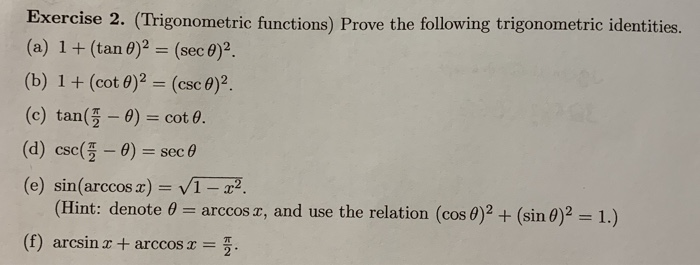



Exercise 2 Trigonometric Functions Prove The Chegg Com




Trigonometric Identities A Plus Topper
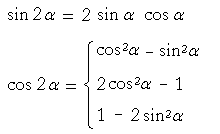



Trigonometric Identities Topics In Trigonometry
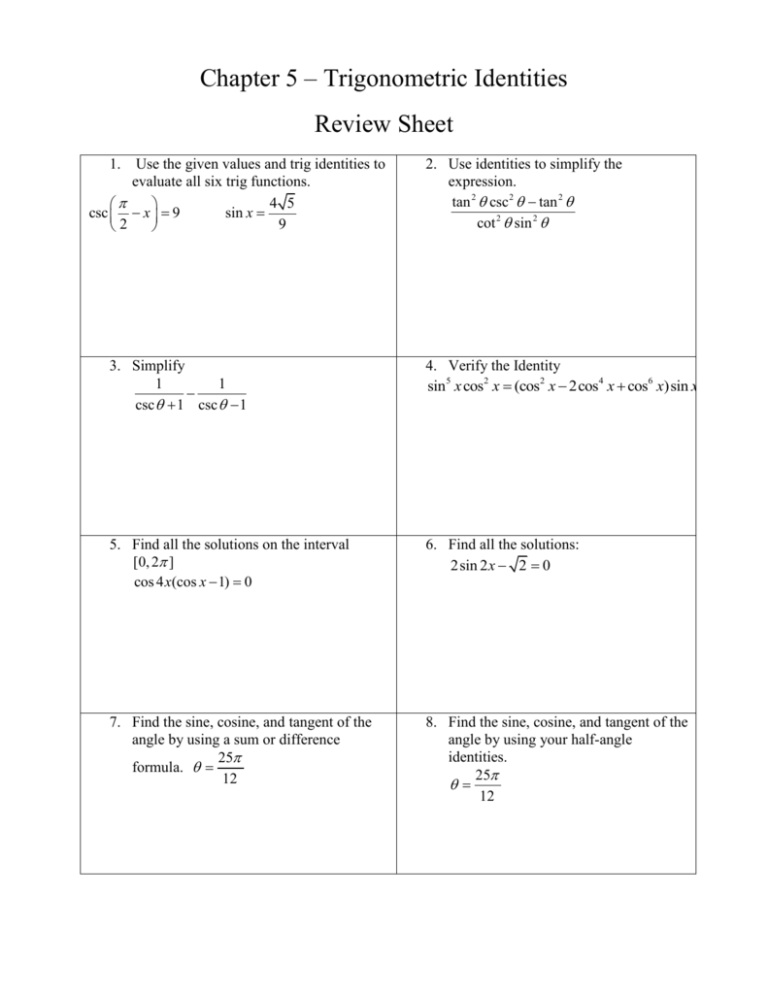



Chapter 5 Trigonometric Identities Review Sheet



Important Trigonometric Identiti



A Trig Identity




Trigonometric Identities



What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora



Solved Trig Identities 1 Sin Cos 2 Sin Cos 2 2 2 Tan2 Cos2 Cot2 Sin2 1 3 Sec Course Hero
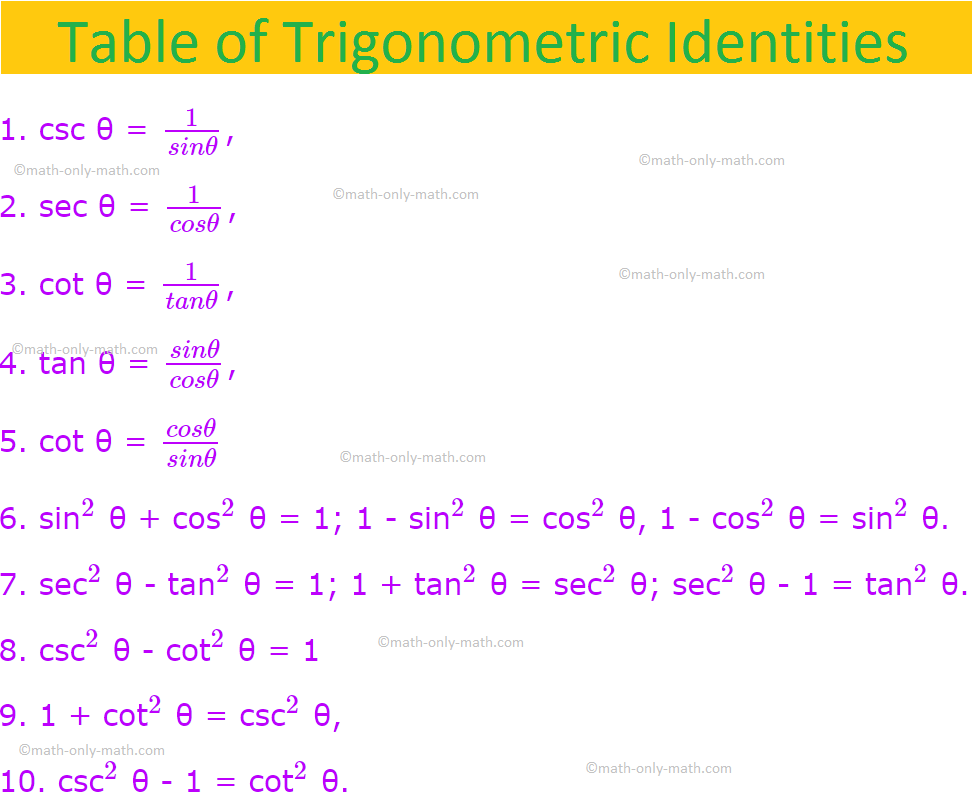



Trigonometric Identities List Of Trigonometric Identities Examples
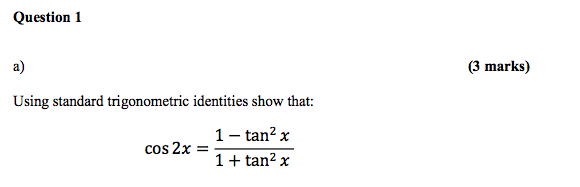



A Using Standard Trigonometric Identities Show That Chegg Com




2 Prove The Following Trig Identities A Prove Tan Chegg Com



Www Brockport Edu Academics Tutoring Docs Trigonometric Identities Pdf
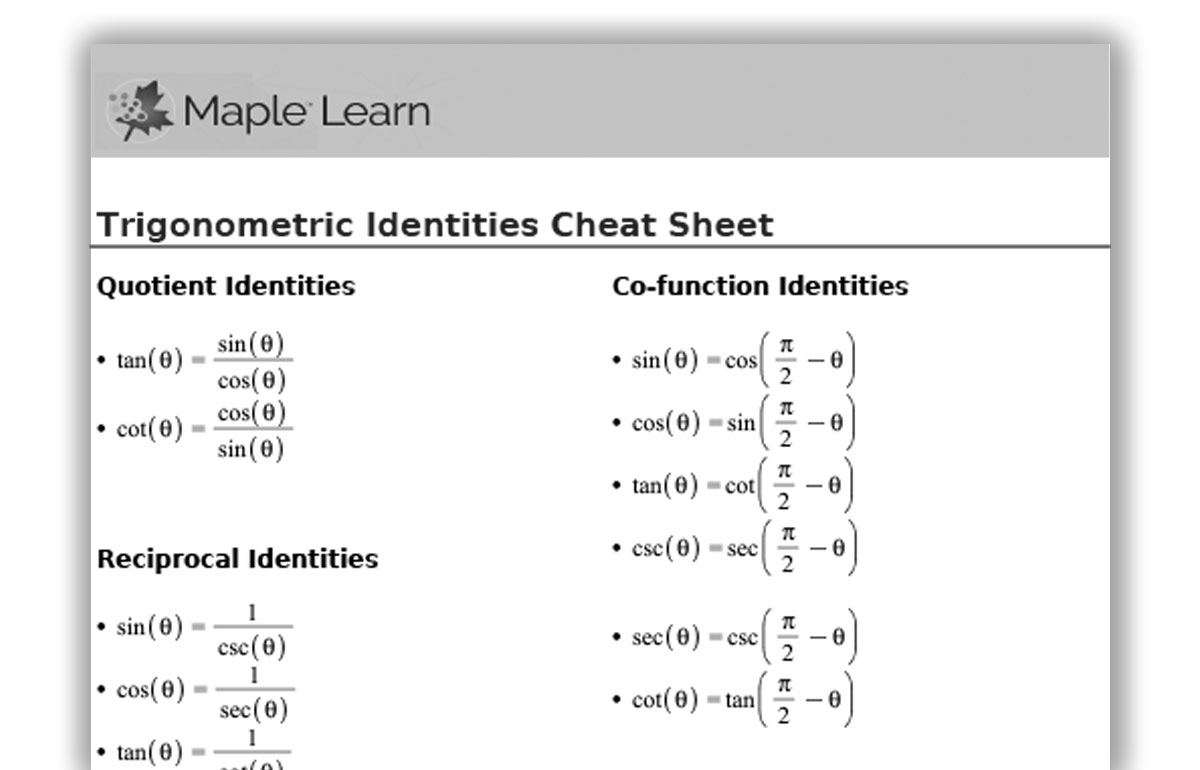



Trig Identities Maple Learn Maplesoft
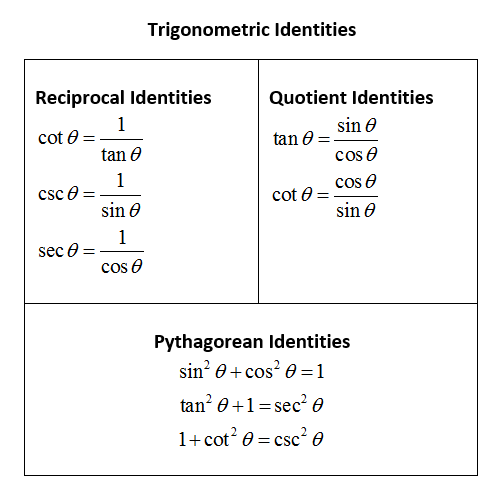



Trigonometric Identities Simplify Expressions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions



1




7 1 Basic Trigonometric Identities And Equations Ppt Video Online Download
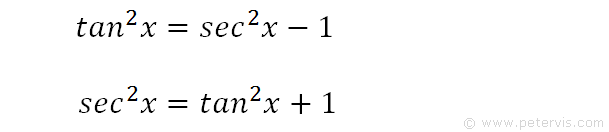



Integrate Sec 2x Method 1



Http Tutorial Math Lamar Edu Pdf Trig Cheat Sheet Reduced Pdf




1 Tan 2x 1 Cos 2x Sin 2x 2sin 4x 1 Sin 2x Trigonometric Identities Mcr3u Youtube




3 1 Reciprocal And Pythagorean Identities Mathematics Libretexts



What Are The Quotient Identities For A Trigonometric Functions Socratic



Http Tutorial Math Lamar Edu Pdf Trig Cheat Sheet Pdf
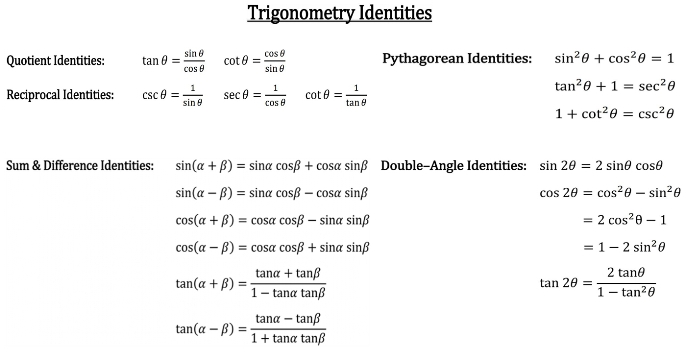



How To Prove Quotient And Reciprocal Identities Studypug




32 Prove The Trigonometric Identity Sec 6 Theta Tan 6 Theta 3 Tan 2 Theta Sec 2 Theta If Sec Theta Tan Theta P Find The Value Of Csc Theta
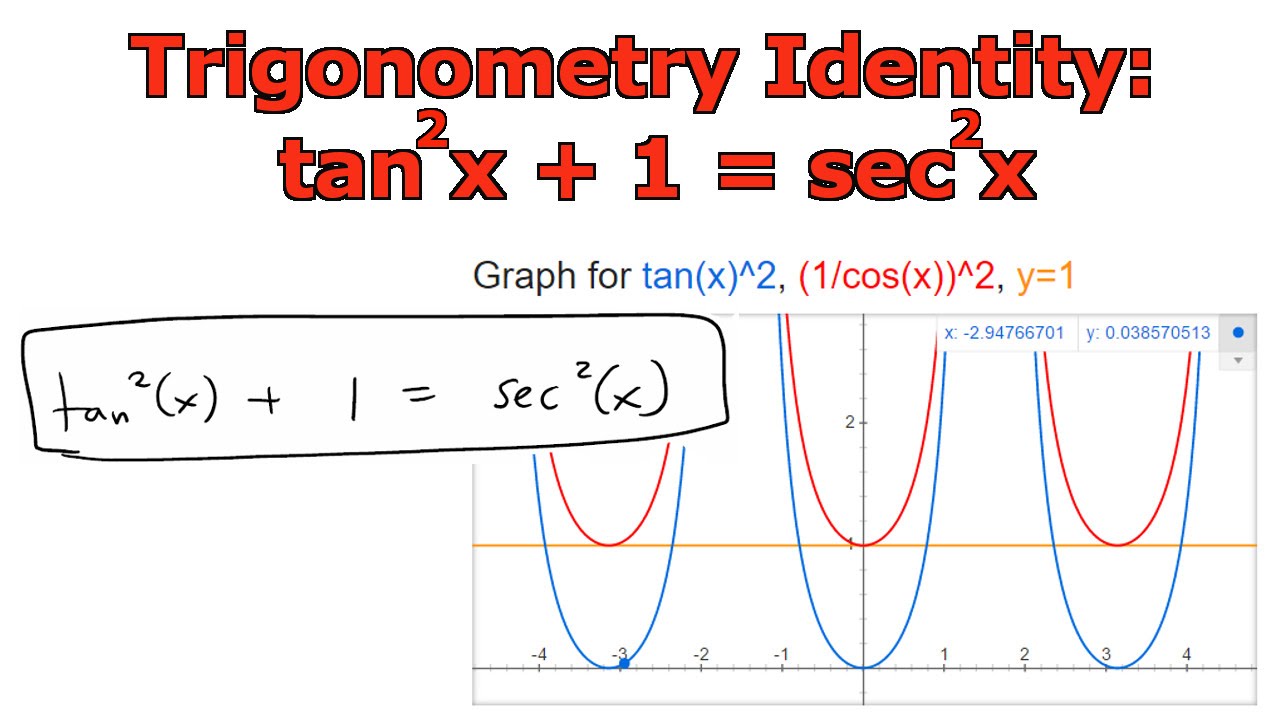



Trigonometry Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec 2 X Youtube



Lt 14 I Know The Trig Identities Blaine High School Precalculus



Complex And Trigonometric Identities Introduction To Digital Filters




Powers Of Trigonometric Functions




5 2 Verifying Trigonometric Identities Copyright Cengage Learning




Ppt Warm Up Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




14 2 Trigonometric Identities



1




Trigonometric Identities 1 Conditional Trigonometrical Identities We Have Certain Trigonometric I Maths Formulas List Simplifying Expressions Maths Solutions




Powers Of Trigonometric Functions




Tangent Half Angle Formula Wikipedia
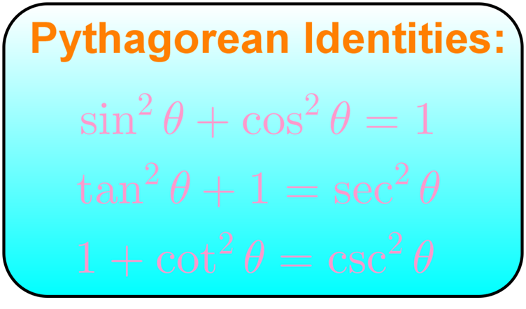



Understanding Pythagorean Identities Studypug
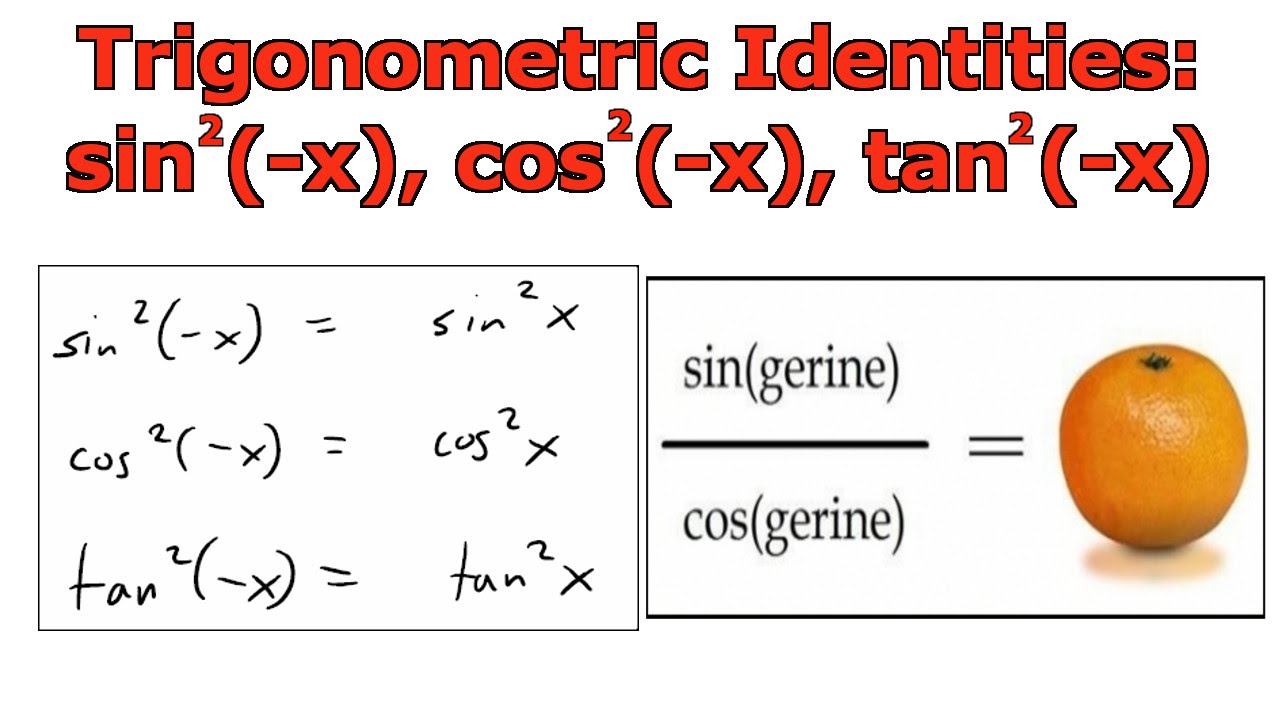



Trigonometric Identities Sin 2 X Cos 2 X Tan 2 X Youtube
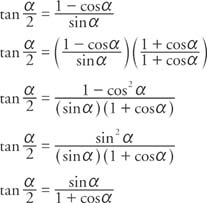



Tangent Identities
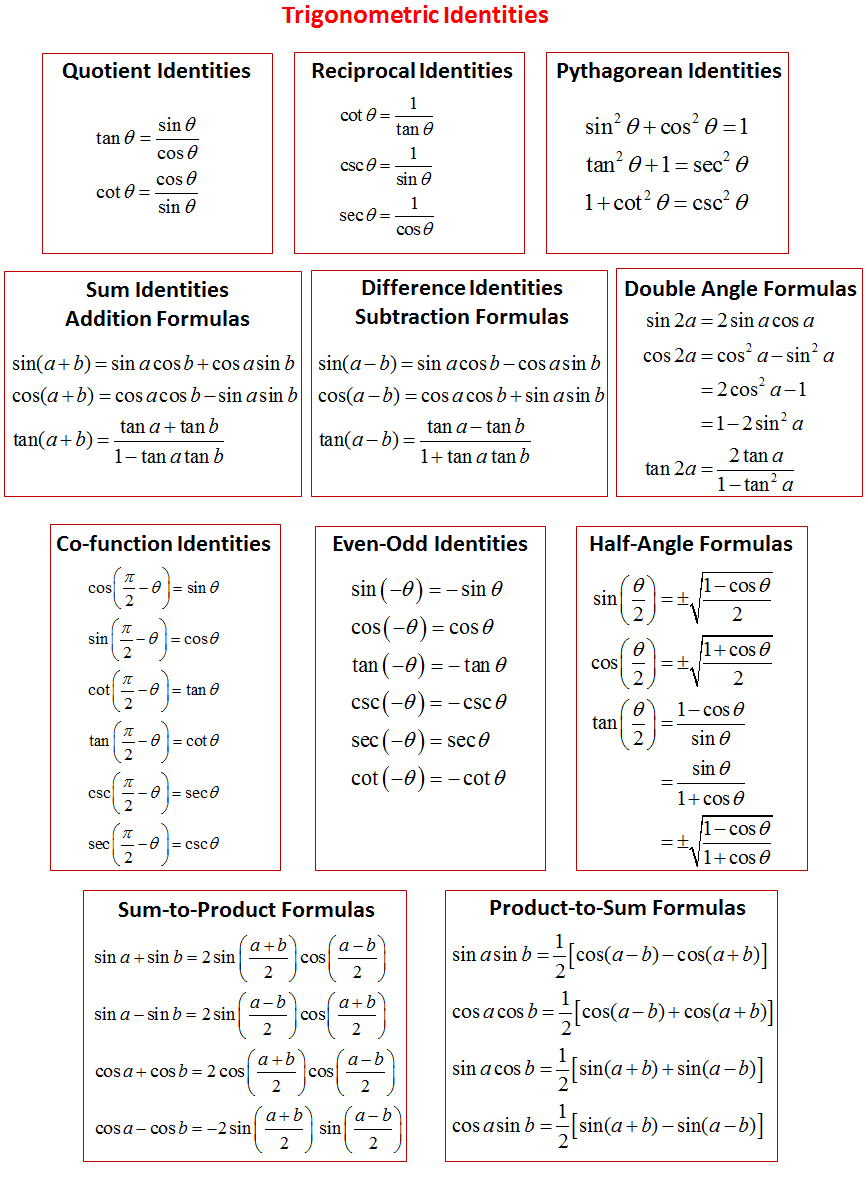



Advanced Trigonometric Identities Solutions Examples Videos



Ilectureonline



Solved Prove The Following Trig Identity Sec 2 X 2secx Cosx Cos 2 X Tan 2 X Sin 2 X Course Hero




Summary Of Trigonometric Identities
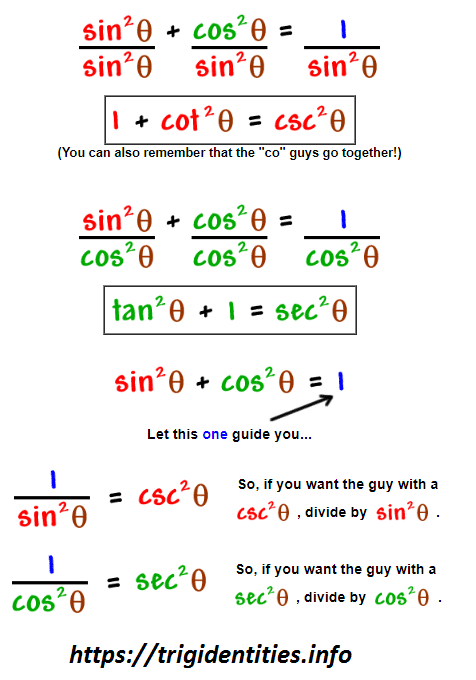



Pythagorean Trig Identities Recall Pythagoras Theorem Trig Identities




Cos Sin Tan Csc Sec Cot




Trig Identities Bingo Card
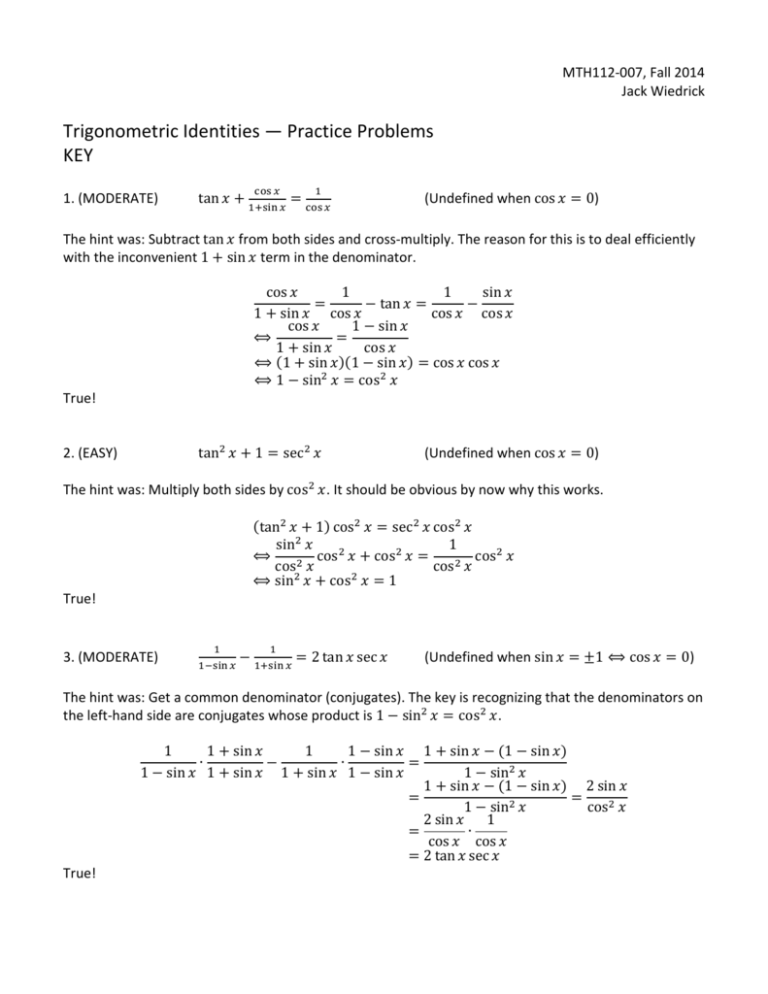



Trigonometric Identities Practice Problems Key
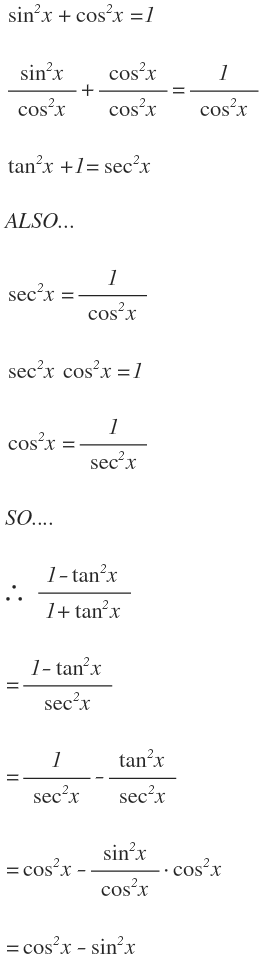



How Do You Simplify 1 Tan 2 X 1 Tan 2 X Socratic
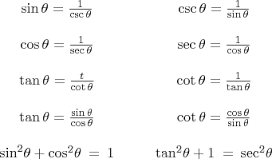



Math Review Of Trigonometric Identities Free Homework Help




Summary Of Trigonometric Identities
x-1=sec(squared)x.jpg)



10 Identity Tan Squared X 1 Sec Squared X Trigonometry Educator Com



Trigonometric Identities A Plus Topper




Fundamental Identities



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿